Man has always wanted to leave his footprints in the annals of time, be it in the current times of selfies or the ancient world, when man was still a hunter-gatherer. And the way they left their imprint was to paint their world, on the walls of their caves and dwelling places.
One of the earliest pieces of art found is the rock paintings and cave paintings of the ancient cave-dwelling men.
Prehistory: Art in Upper Palaeolithic age – (50,000 years to 12000 years ago)
In 2006 in France, archeologists found, in a cave near Angoulême in western France, what they believe is one of the oldest specimens of rock painting of a human face, maybe one of the oldest examples of portrait painting in the world.
 Vilhonneur Grotto Cave Rock Portrait
Vilhonneur Grotto Cave Rock Portrait
The facial features are drawn with calcium carbonate in black on a wall using the bumps in the wall to give it the form of a human face. It could be the first recorded portrait painting in the history of mankind. Archaeologists claim that the drawings in the cave were done 27,000 years ago, which makes the Vilhonneur Grotto one of the oldest sites of rock art in the world.
Similarly, in India, one of the oldest rock paintings art has been found in the Bhimbetka cave paintings, which are thought to be 30,000 years old. Amalananda Ghosh, a noted Indian archaeologist, wrote in his book, An Encyclopedia of Indian Archaeology, “There can be no doubt that pigment from these nodules was used for painting. A part of the painting is therefore clearly associated with Mesolithic hunter-gatherers.”
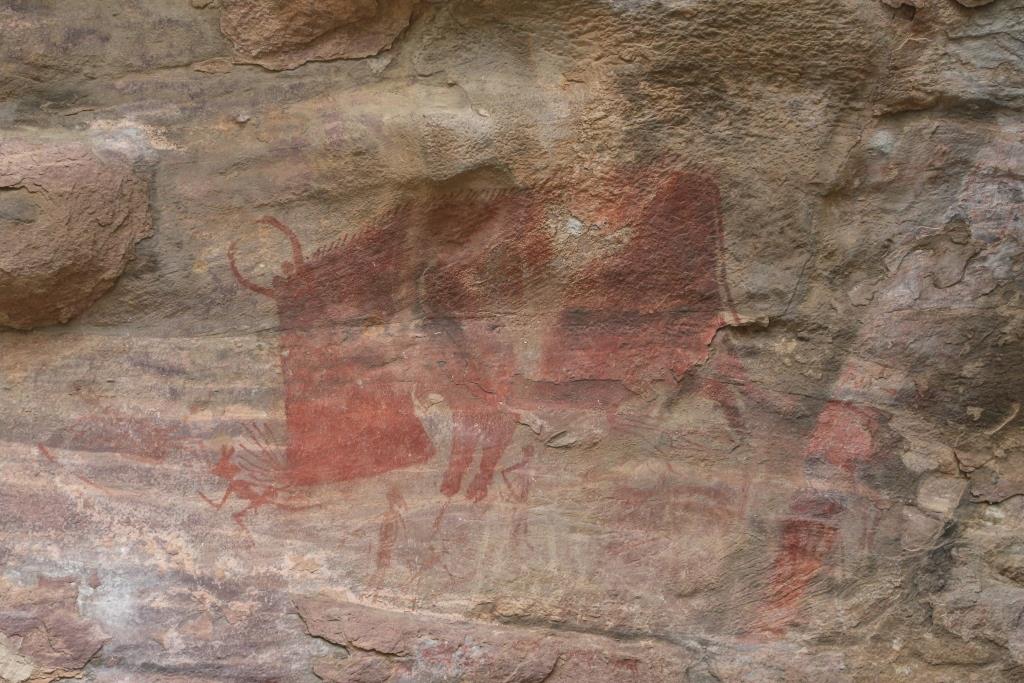 Bhimbetka Rock Painting
Bhimbetka Rock Painting
Another well-known archeologist, Col. DH Gordon, wrote in his book, Prehistoric Background of Indian Culture, in 1939, “There is, in fact, no feature of their life which is not depicted in these paintings, but because they are clearly of no great age, they have not attracted the notice they deserve.”
Researchers, since then have firmly established these paintings can be as old as 30000 years, making the caves the oldest art gallery in India.
These prehistoric rock paintings and portraits are considered to be one of the earliest examples of art and painting in the history of mankind.
Order Your Portrait Painting from Photo today!
Classical Era: Art and Painting in the classical age
Ancient cave paintings gave way to more modern portrait murals and frescoes. Noted examples of ancient murals have been found in Egyptian tombs around 3150 BC, Minoan palaces 1700-1600 BC, AND Pompeii 100 – 200 BC.
Similar examples of ancient art, murals, frescos, and portrait painting were found in India, in the caves of Ajanta (Modern day Maharashtra), Ellora (Maharashtra), Bagh caves (Madhya Pradesh), Armamalai caves (Tamil Nadu), and Sittanavasal cave (Tamil Nadu).
The caves include paintings and rock-cut sculptures described as among the finest surviving examples of ancient Indian art, particularly expressive paintings that present emotions through gesture, pose, and form.
 Ajanta Bodhisattva
Ajanta Bodhisattva
The main theme of the paintings is the depiction of various Jataka stories, different incidents associated with the life of Buddha, contemporary events, and social life. The ceiling decoration invariably consists of decorative geometrical and floral patterns.
The Middle Ages: Art and Painting in the medieval age
The art and paintings of the middle ages covered the period from the fall of the Roman Empire in 476 AD to the early stages of the Renaissance period in the 14th century.
In the period from 476 AD and over the next 1000 years, the art world developed at a rapid phase and prolific output with a diverse range of artistic styles and eras. Some of which include early Christian & Byzantine art, Anglo-Saxon art, and Gothic art. Medieval artists and their paintings predominantly portrayed holy figures and biblical narratives.
 Meister des Benedictionale des Baptism of Christ
Meister des Benedictionale des Baptism of Christ
During the same period when medieval art was developing rapidly in Europe, art was making considerable progress in India too. Just like in European art, Indian artists and artisans evolved to make religious art and Royal families as their focus. During this period Indian art flourished under major empires like Mauryan Empire, Gupta Empire, and Chola Empire.
Order Your Custom Handmade Oil Portrait Painting from Photo today
Early Modern Era (1450 AD – 1750 AD)
The early modern era marks the modernization of visual art and paintings as we know them today, and is generally accepted to be the period of AD 1450 – AD 1750. This is also the period we are most familiar with. The idea of Europe as a separate cultural and civilizational identity germinated in this period. Some of our most modern ideas and thoughts of art, culture, philosophy, music, science, and politics like Humanism, the European Renaissance, and The Age of Enlightenment were born and nurtured during this period.
This period marks the transition of Europe from the medieval period to the early modern age. We are intimately familiar with the artists from this period like Sandro Botticelli, Michael Angelo, Leonardo Davinci, Raphael, Donatello, Caravaggio, Giovanni Bellini, and Jan van Eyck.
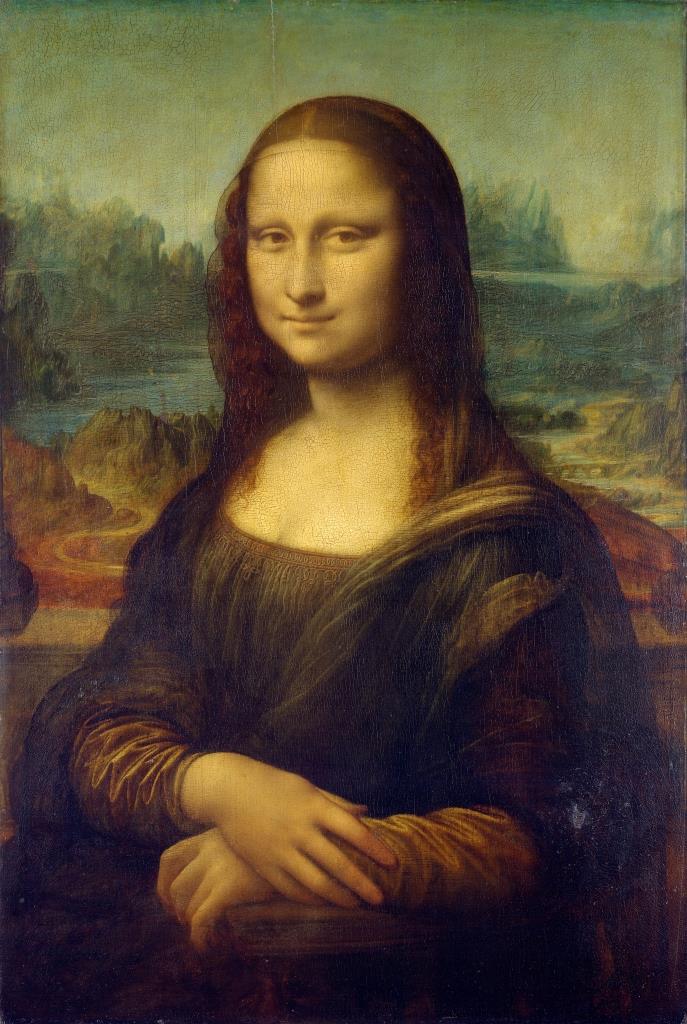 Mona Lisa Portrait Painting by Leonardo da Vinci
Mona Lisa Portrait Painting by Leonardo da Vinci
Handmade Art Reproductions & Landscape Paintings
The art of this period came to be known as the classical period. The paintings of this period moved from the rigidity of the earlier periods to a more realistic depiction of subjects. Oil as a medium of painting was widely known at this time. Some of the best paintings done during this period were oil paintings. While the artists of the earlier periods were mainly concerned with the depiction of religious figures and icons, the new generation of artists of the Renaissance period focussed on the realistic depiction of their subjects in their paintings. The art of portrait painting also became well known during this time, with artists executing commissioned artworks like portrait paintings and oil paintings. The classical period was followed by the Baroque Style, which in turn was followed by the French Classicism (also known as Louis XIV) style, which gave way to the Rococo style.
Art also moved from palaces and churches to the wealthy and the nobility. Oil painting art and portrait paintings also got a fillip during this era. Some of the most important pieces of art of this period were oil paintings and portrait paintings, like Mona Lisa by Leonardo Davinci, Portrait of Eleanor of Toledo by Bronzino, The Ambassadors by Holbein, and the Pelican Portrait of Queen Elizabeth I by Hilliard.
The oil paintings and portrait paintings of the Early modern era period were characterized by exploration of space, delineation of backgrounds, and strength of colors, with strong and moving characterizations of subjects.
While the European art scene and painting styles progressed rapidly during this period, Indian art and painting styles were also changing rapidly with the advent of the Islamic age.
With the Islamic conquest of India, Indian art styles and paintings underwent distinct changes in their character, styles, and depictions. While the earlier artists were mainly concerned with religious paintings, the influx of the Persian style of painting created a distinct character of their own, now identified as Mughal art.
Emperor Humayun of the Mughal Empire brought two of the finest artists of that time from Persia, with him, Mir Sayyid Ali and Abd al-Samad. Under their supervision, several Indian artists were trained in the Persian style of painting.
But the Mughal style of creating portrait paintings and oil paintings came into its own during the reign of Akbar and later his successor Jahangir. Works of the court painters during this period incorporated various Indian elements of flora and fauna which were absent in the traditional Persian style paintings. The Mughal style of painting was heavily influenced by Persian and Islamic miniature styles of painting, and in turn, they influenced other Indian painting styles like Rajput painting, Pahari painting, and Deccan style painting. While the earlier Persian styles of painting were stiff in their appearance, the Mughal style of painting became more fluid and naturalistic under the influence of Indian artists.
Like kings and emperors before them, the Mughal emperors and their descendants wanted a visual record of their deeds as conquerors and hunters for posterity. Books like Akbarnama (Book of Akbar), commissioned by Akbar, Baburnama, (History of Babur), and Hamzanama, (exploits of Amir Hamza) not only recorded their exploits but also served as a visual record of their courage, strength, and royal persona. These illustrated books of the reigns of the Emperors gave rise to the need for skillful portrait painting artists. Persian artists trained their Indian counterparts in the nuances of portrait painting in the Persian style of oil painting. Thus the need for a visual record of the emperors gave a fillip to the fine art of portrait painting and miniature painting.
 Illustration from the Akbarnama by Basawan
Illustration from the Akbarnama by Basawan
Some of the notable portrait painting artists and painters during this era were Basawan, who worked on the illustrations and portrait paintings of Akbarnama. Manohar Das, son of Basawan who worked in the service of Jahangir, Govardhan who worked on the illustrations of Baburnama, and Bishandas who worked in the reign of Jahangir and was sent to Persia to work on the portrait painting of Shah Abbas I of Persia. Other notable artists from the Mughal period were Abu al-Hasan and Daulat.
Alongside Mughal style paintings several other styles of painting developed in conjunction with and along with Mughal paintings. Prominent among them are Deccan painting, Rajput Painting, Pahari paintings, Malwa & Jaunpur styles, Mysore paintings, Tanjore paintings, and Pattachitra and Madhubani painting styles.
Modern Era (AD 1750 AD present)
The period after AD 1750 till the present is generally accepted as the modern era. Keeping with the age of the times, art and paintings also progressed taking inspiration from the Early Modern art movements. Several styles of painting developed during this era and continue to develop to this day.
The Modern Era is further divided into:
NeoClassicism (1760-1800)
Romanticism (1800-1850),
Modern Art (1860-1970) and
Contemporary art (1970-till date), the current period
NeoClassicism (1760-1800)
Neo-Classicism was an art and cultural movement which began in the early 1760s, inspired by the classical antiquity period between the 8th century and 6th century when the interlocking Greco-Roman civilization of Greece and Rome were at their peak.
In the backdrop of the Age of Enlightenment, the rediscovery and revival of the Greco-Roman style of art and painting were mainly due to the pioneering efforts of Johann Joachim Winckelmann, considered by many as the father of modern archaeology and father of Art history. His book History of Ancient Art, one of the earliest books written in German has become a classic in European literature.
European artists adopted the Greco-Roman style of painting, as a reaction to opposing the then-dominant Rococo style, which emphasized ostentatious ornamentation and grace.
The guiding principles of Neoclassicism were simplicity and symmetry.
Pioneering artists of Neo-Classicism were Jacques Louis David, Antonio Canova, Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres, Angelica Kauffman, and William Adolphe Bouguereau. Many of their oil paintings, even today are considered masterpieces with students encouraged to copy their style as a part of the training in techniques of portrait painting and oil painting.
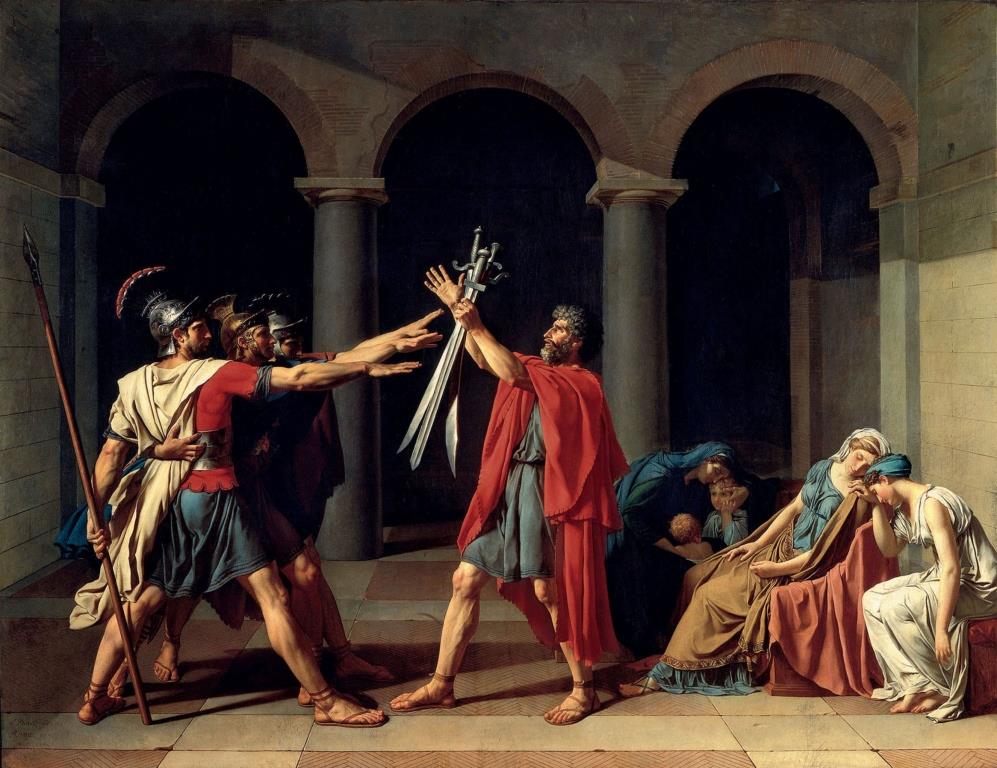 Oath of the Horatii Painting by Jacques Louis David
Oath of the Horatii Painting by Jacques Louis David
A few artists like Dominique Ingres and Angelica Kauffman were also skillful portrait artists who created numerous oil portrait paintings in neoclassical style and were known for their mastery over the art of making different types of portraits.
Romanticism (1800-1850)
Romanticism was an art movement that originated in the late 18th century in Europe. It emphasized individualism, emotions, and subjectivity over rationalism, science, and classicism of the Enlightenment period.
Born as a reaction to the Industrial Revolution and the constraints of rationalism, Romanticism sought to promote experiences such as fear, horror, and terror over the sublime beauty of nature.
The key principle of Romanticism was creativity and the creation of original work from nothingness derived entirely from the artist’s imagination.
 Saturn Devouring His Son Painting by Francisco Goya
Saturn Devouring His Son Painting by Francisco Goya
Pioneering artists of Romanticism were Francisco Goya, Caspar David Friedrich, Eugene Delacroix, Theodore Gericault, Ivan Aivazovsky, and Francesco Hayez. Many of the oil paintings of these great masters are found housed in museums around the world.
“Kampani Kalam” or the Company Style
As art moved from the classical period to the modern era in Europe, Indian art also moved along with the political developments of the time.
The Mughals gave way to the European colonialist powers like the British, the Portuguese, and the French, which colonized India after the Mughal rule came to an end.
The art produced during the period gave a visual record of India in European sensibilities and came to be known as the “Kampani kalam” or the Company Style, named after the British East India Company, which eventually came to colonize India. The painting style of the era was a hybrid Indo-European style painting, which married the elements of the Rajput and Mughal styles of paintings with the European style of painting. Indian artists adapted the European style of oil painting and replaced the traditional bright colors of Indian paintings with muted colors and hues in their oil painting and portrait painting works, which appealed to European sensibilities.
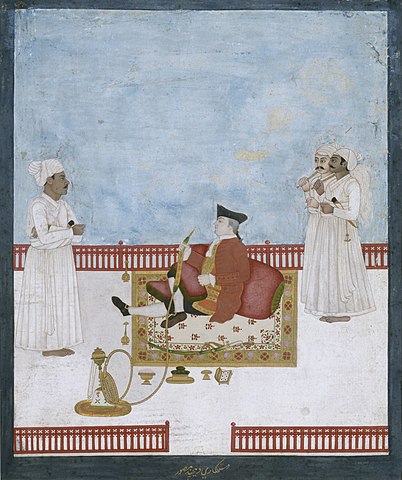 Portrait of East India Company Official Company Style
Portrait of East India Company Official Company Style
Shaikh Muhammad Amir of Calcutta, Shiva Lal, and Shiva Dayal Lal (from Patna school of company painting), were some of the well-known artists of that era. With the demise of Ishwari Prasad of Patna, the company style of oil painting came to an end.
Modern Art (1860-1970)
The modern art movement is arguably one of the most important art movements in recent art history. Not only did it give birth to new styles of art, but also art moved from the ruling nobility to the bourgeois class. The era of modern art gave rise to a series of art movements in rapid succession which left an indelible impact on the art world.
Notable art movements during the period were
Impressionism
The art movement derives its name from Claude Monet’s oil painting work Impression, Soleil levant (Impression, Sunrise). The movement started mainly in France, when in early 1860 artist Claude Monet and his friends, Frédéric Bazille, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Alfred Sisley started painting landscapes and contemporary life, usually in the countryside outside the studios. The oil painting style was of short thin brush strokes, with a focus on light and its accurate depiction, with an emphasis on freely brushed colors overdrawn lines, and outlines.

Impression, Sunrise Painting by Monet
Noted artists of the Impressionist movement were Claude Monet, Eduard Manet, Pierre Auguste Renoir, Edgar Degas, Henri Matisse, Camille Pissarro, and John Singer Sargent.
Among them, John Singer Sargent, an American artist, was considered the leading portrait painter of the time. His portrait paintings had a delicate touch and an unmistakable air of elegance. He considered his portrait painting titled Portrait of Madame X, his finest work, even though the oil painting did not receive much acclaim at the time. His other famous work was the portrait painting of Lady Agnew of Lochnaw. The oil painting was made when Lady Agnew was recovering from the flu.
Post Impressionism
The art movement emerged around 1886, as a reaction to the Impressionism art movement with its over-emphasis on the naturalistic depiction of light and colors. Mainly a French art movement, the term was first coined by art critic Roger Fry, in 1906 in an exhibition catalog. Post Impression emphasized the usage of vivid colors, using impasto, and geometric forms while retaining certain characteristics like painting from life. The movement lasted from 1886 to 1905.
Although there is no cohesive force to define the Post-impressionist movement, except perhaps that the artists exhibited together, John Rewald American author and art historian wrote,” Post-Impressionism' is not a very precise one, though a very convenient one”
While academically the movement may have been not very well defined, the artists of the era certainly redefined art.
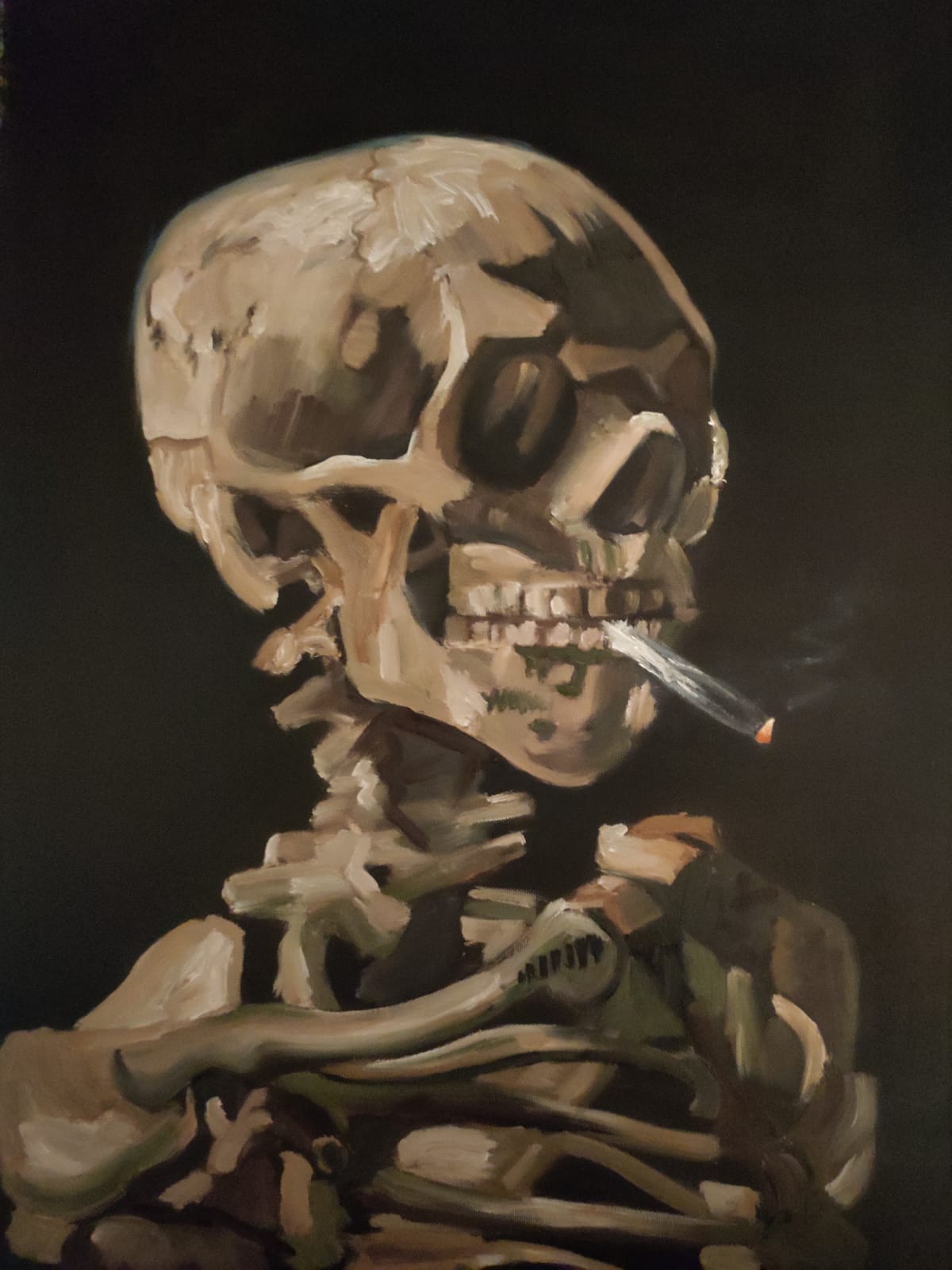 Van Goghs 'Skull of a Skeleton with Burning Cigarette',
Van Goghs 'Skull of a Skeleton with Burning Cigarette',
Custom handmade oil painting reproduction by Paintphotographs.com
Famous artists of the era were Paul Cézanne, Vincent Van Gogh, Paul Gauguin, Georges Seurat, and Henri Rousseau. Their oil painting works continue to inspire today’s artists. Particularly Van Gogh's self-portrait paintings, which are highly valuable works of art.
Expressionism
Expressionism was a modernist art movement between 1905-1920, which flourished in Northern Europe, especially in Germany and Scandinavia. The Expressionist art movement emphasized individual perspectives and emotions and sought to express man’s inner angst.
The Expressionist art movement mainly sought to evoke an emotional experience, rather than physical resemblance.
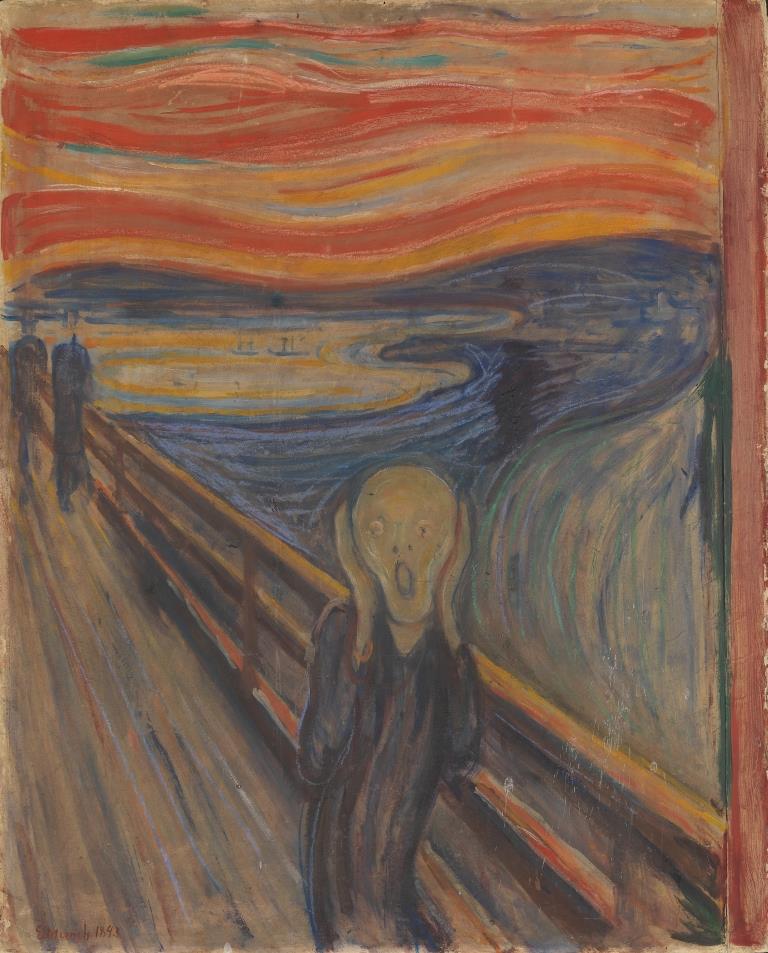 The Scream, Painting by Edvard Munch
The Scream, Painting by Edvard Munch
Noted artists of the expressionist movement were Edvard Munch, Wassily Kandinsky, Otto Dix, Marc Chagall, Franz Marc, and Ernest Ludwig Kirchner.
Cubism
Cubism, an avant-garde art movement emerged in the early 20th Century. Pioneered by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, it is considered one of the most important, radical, and influential art movements of the 20th century. The movement lasted from the late 1900 to the early 1920s.
While earlier artists would render a depiction of an object on canvas as realistically as possible, a cubist approach is to reduce the object to its geometric shapes and render them on canvas from different sides and angles. Somewhat like looking at an object through a Kaleidoscope in all its fragments. This way, the cubist feels, he is better able to give an understanding of the object. Depicting an object or subject in this manner on the canvas, which renders the object both flat and solid, was a completely new way of looking at things since the classical days of antiquity. This novel and radical way of looking at the world completely revolutionized the art world.
Offshoots of cubism developed with Orphism, abstract art, and Purism. Other art movements also developed in response to Cubism like Futurism, Dada, and Constructivism.
 Old Guitarist Painting by Pablo_Picasso
Old Guitarist Painting by Pablo_Picasso
Pioneering artists in the field of cubism were Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque, Juan Gris, Albert Gleizes, Jean Metzinger, and Robert Delauney.
Early Modern Indian painting
Company style of art and painting gave way to modern Indian painting. Formal schools of art were established to educate and train students in art, namely Government College of Fine Arts Madras 1850 Madras (now Chennai), Government College of Art & Craft 1854, Calcutta (Now Kolkata), J.J School of Arts Bombay (now Mumbai) 1857.
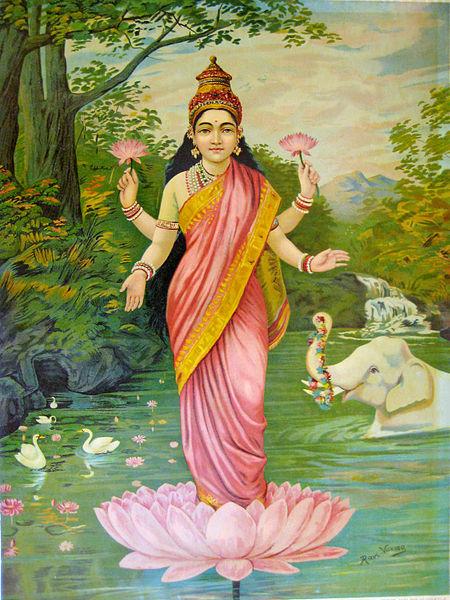 Lakshmi the goddess of wealth oil painting by Raja Ravi Varma
Lakshmi the goddess of wealth oil painting by Raja Ravi Varma
Raja Ravi Varma (1848-1906) is considered the pioneer of Indian painting. He married the neo-classicism of Western Art with Indian sensibilities and traditions. A self-taught artist his portrait paintings and his oil paintings are considered classics even today. His subjects were purely Indian such as Hindu deities and episodes from the great Indian epics like Mahabharata, Ramayana the Puranas, portrait paintings of Maharajas, and oil paintings inspired by daily life. While in the West neoclassical style was considered anti-modern, it was new in the context of Indian art and painting style. He is regarded widely as the first Indian modern artist to have built up a pan-Indian following. Through his oil paintings and mass-produced oleographs, he managed to reach out to the mass of emerging middle class and managed to transform the formal Western academic style of realism into urban pop culture. Such was his impact, that the Devis and Devtas painted by him are still very popular.
Bengal School
Post the period of Raja Ravi Varma, the mood of the nation changed. The political climate became rebellious as Indians sought political Independence from the oppressive and exploitative British rule. Cries of Swaraj and Swadeshi rent the air as nationalism took center stage.
The Bengal School of Art emerged in the early 20th century as a reaction to the political environment against the colonial influence of the times. The avant-garde art movement started in Calcutta (Now Kolkata), and Shantiniketan but soon spread to the rest of India. Led by Abanindranath Tagore, the creative impulses of artists took a decidedly nationalistic turn.
Noted art historian, art critic, and curator, R Siva Kumar noted, “In the arts, this meant, a rejection of academic realism, as an anti-colonial gesture, and revival of indigenous values and forms.”
Although the artistic styles in Bengal School were individualistic, some of the elements were common among them. The use of earthly dark and muted colors, the use of indigenous materials like tempera, and limited shades and color palette are some of the characteristics of the art movement.
 Bharat Mata Painting by Abanindranath Tagore
Bharat Mata Painting by Abanindranath Tagore
One of the most famous artworks of the period was Bharat Mata, by Abanindranath Tagore, where the artist imagined India as Mother India and depicted her as a young woman with four hands holding objects of India’s national aspirations. The painting was stylized in the manner of Hindu Goddesses as depicted in the Hindu mythologies.
Famous artists who emerged from the Bengal School of Art movement were Abanindranath Tagore, his brother Gagendranath Tagore, Sunayani Devi, the sister of Abanindranath, Nandalal Bose a disciple of Abanindranath Tagore, Asit Kumar Halder, Kalipada Ghoshal Mukul Dev, and Manishi Dey
Eventually, the Bengal School of Art movement gave way to Modernism. Modernism in the context of Indian art was inspired by the pan-Asian art styles while retaining the broad conceptual Western framework. Revivalist in its influence, Modernism in Indian art drew inspiration from Japanese art, folk, and the traditional art of India. Rabindranath Tagore is the first artist to be considered a Modernist Internationalist, influenced by Western impressionists and surrealists. However, artists like Nandalal Bose, Amrita Shergil, and Jamini Roy were considered to be at the forefront of the movement of Modernist art in India along with artists like Benodebihari and Ramkinkar Baij.
Post-independence Progressive art schools
In the 1940s a new art movement started in India, called the Progressive Artist Groups. Although started around 1940, it is widely considered the post-Independence art movement. The decade of 1940s saw the emergence of art groups in Calcutta (Kolkata), Madras (Chennai), and Bombay (Mumbai)
First formed in Calcutta in 1943, the Calcutta Group, followed by the Progressive Artist Association in Madras (Chennai) in 1944, and the Progressive Artist Group in Bombay (now Mumbai) in 1947.
The Calcutta Group
The Calcutta art group was formed by Subho Tagore in 1943 in Calcutta (now Kolkata). The group has the distinction of being the first art movement in India of its time. Other members of the group were Nirod Mazumdar, Gopal Ghosh, Paritosh Sen, and Kamala Dasgupta. The group was disbanded in 1953. Though short-lived, it was the first artist group to bring contemporary Indian art to the world stage. Their choice of medium usually was an oil painting and watercolor.
Progressive Artist Association in Madras (Chennai)
Started by Colonel Alexander Hunter in 1850 as a private institution, the Madras School of Arts and Crafts was taken over by the British Government in 1959. In 1963, post-Independence, the college was renamed as the Government College of Arts and Crafts.
A renowned artist of Bengal, Devi Prasad Roy Choudhury, took over as the Principal of the college. After Devi Prasad Choudhury’s retirement in 1957, KCS Paniker took over as the Principal.
It was Paniker who pioneered the Progressive Artist movement in Madras (now Chennai) in 1944. In the post-Independence period, as artists strived to create their own identities, beyond colonialism, the focus shifted from the Nation to the individual. Their oil painting works are considered classics today in the Indian art world. Paniker’s painting also moved to more Humanist and contemporary themes. In 1966 he formed the Cholmandalam Artist Village, which is the largest artist commune in India.
In Chitram Ezhuthu: a publication on art and letter, artist KK Hebar wrote, “As Principal of the Madras School of Arts and Crafts, Paniker could wield his influence over a large number of young artists. After retiring from service Paniker gathered quite a few of these talented artists- both painters and sculptors and established an envious art complex “Cholamandal” –the first of its kind and also perhaps the best in the country. This artists’ village in the vicinity of Madras is a living monument to keep Paniker’s memory fresh for a long time to come. I take this opportunity to pay my compliments to his unique personality.”
Although formed in 1944 by the Progressive Artist Association in Madras (now Chennai) the movement flourished from the 1950s to the 1980s.
The Progressive Artist Group Bombay
The Bombay Progressive Group (PAG) was the last to be formed in 1947, but it was the most successful and influential in asserting its modernist ideals. The group was founded by artists like Francis Newton Souza, Maqbool Fida Husain, Syed Haider Raza, Krishna Hawlaji Ara, Hari Amba Das Gade, and S. Bakre. Other artists like Akbar Padamsee, Tyeb Mehta, Bal Chhabda, Vasudeo S Gaitonde, Ram Kumar, and Krishna Khanna were closely associated with the group.
The group produced many oil painting works during the period. Even after the group disbanded the oil painting works continue to draw inspiration and appreciation from the art world.
Perhaps the most well-known artist of the group was MF Hussain. A prolific but controversial painter, also known as the barefoot artist. His oil painting works like Mother Teresa, Madhuri Dixit, and paintings of horses bought him much acclaim while his other oil paintings like Bharat Mata and paintings of Hindu Devis bought him many controversies.
The other artists in the group, Souza, Tayeb, Raza, and Gaitonde, became equally well-known and leading artists of their times. Their oil painting works today command hefty prices and is sought by art collectors for their prized collections.
About the group, R Siva Kumar writes. “This group began with a leftist ideological self-imposition, but ‘progressive’ soon came to mean for them a modernist use of formal elements, inspired by modern Western Art. Rather than develop indigenous Modernism, they believed the right thing for the Indian artist was to assimilate the language of modern art and become a part of International modernism. As the representative of a newly independent country committed to Industrialization, this appeared to them as the historical need of the hour.”
Contemporary art (1970-till date), the current period
While Indian art and artists were actively defining new art styles and painting movements in India, after Independence. Europe after World War II struggled to rebuild itself from the ashes of the World Wars. As a result, the art world’s focus shifted to the United States, as America became a preeminent political, economic, and military power in the World. And New York took over as the capital of the Western art world from Paris.
Many important contemporary art movements and painting styles developed during this time in America, some of the more popular styles were Abstract Expressionism, Pop Art, Minimalism, and Photorealism.
Abstract Expression
Abstract Expressionism was the first art movement that developed in New York in the 1940s to achieve international acclaim and influence. And made New York the new center of the Western art world, a place that was previously occupied by Paris in France.
Paul Jackson Pollock is now widely recognized as the artist, who with his “drip technique” brought the Abstract art movement into focus and to international acclaim.
Also known as “all-over” painting or “action painting”, in the “drip technique” the artist splashes liquid color all over the canvas, which is kept on the floor or a suitable flat surface. The technique allows the artist to attack the canvas from all angles. Paul Jackson’s technique divided the art critics of the time. Some praised the immediateness and spontaneity of the creation and others derided and disparaged the chaotic and random brush strokes and chaotic effects.
While Jackson Pollock was considered the leader in Abstract Expressionism, other notable and acclaimed artists of the Abstract Expressionist movement were, Mark Rothko, Williem de Kooning, Franze Kline, Helen Frankenthaller, and Lee Krasner. Many of the oil painting works of these artists today are found in private collections or prestigious museum collections.
Pop Art
The term Pop Art was first used by art critic Lawrence Alloway, in the United Kingdom in 1956, to refer to the new art movement which celebrated the consumerist culture of the post-war era in the UK. The movement focussed on the exuberance of consumer culture, often depicting material from pop culture, advertising, and motifs from the mass production and consumption culture of the time. Pop art merged objects of popular mass culture, and kitschy elements of everyday life with fine art while infusing them with a sense of humor, playfulness, irony, and everyday emotions. The movement developed as a reaction to the earlier Abstract Expressionism art movement, which dealt with more dark, weighty, and serious subjects like the human psyche.
While Pop art started in England, it gained its popularity and international appeal in the US on the back of popular artworks and paintings by artists like Andy Warhol, Jim Dine, Wayne Thiebaud, and Roy Lichtenstein. Like their counterparts in the UK, the artists of the US, also used everyday objects, kitschy elements of popular culture, and advertising material and infused them with comic book style of panel storytelling and playfulness to make their art.
PhotoRealism
Photorealism as an art form or a painting style developed from the Pop art movement which preceded it during the late 1960s and early 1970s in the United States as a counter-reaction to the Abstract Expressionism and the Minimalist art movement.
Photorealists use photographs as the source material for making paintings and attempt to recreate the image as a painting on canvas as realistically as possible. Usually, these types of paintings are created as oil paintings.
The term Photorealism was first coined by noted author and art dealer Louis K. Meisel in 1969 and appeared in print in the Whitney Museum catalog for the show “Twenty-two Realists” in 1970. This style of artwork and painting is also known as Super Realism, New Realism, Sharp Focus Realism, or Hyper Realism.
This type of painting requires a photograph to make the painting. The artist then uses the reference photograph to create the oil painting on the canvas. Creating oil paintings of this type requires rigorous training and a high level of technical prowess with mastery over reflectance, and angular congruence, and the style needs to be precise and tight.
Mainly used for making a portrait painting from a photo, the photorealism style of painting naturally lends itself to creating memorial oil portraits, family paintings, anniversary portraits, and other life events.
Some well-known first-generation artists who pioneered the Photorealism art movement were American painters like Richard Estes, Chuck Close, Audrey Flack, Charles Bell, Robert Bechtle, Ron Kleemann, John Salt, and Tom Blackwell.
The art movement which started in America has now moved beyond the country and gone international, with many European artists joining the movement. Contemporary artists, like Clive Head, Raphaella Spence, Bertrand Meniel, and Roberto Bernardi are considered leading artists of the Photorealism movement.
Several other important art movements developed during the contemporary times which need to be mentioned like Surrealism, Fauvism, Dadaism, Primitivism, Colour field painting, Postmodernism, Postminimalism, and digital art.
Conclusion
In this article, we have tried to cover as much as possible the History of paintings and portraits through the ages starting from prehistoric times to the Palaeolithic age of cave paintings and wall paintings down to our current contemporary age.
We have attempted to capture histories and timelines of the development of various forms, schools, and techniques of painting both in India and in the West and how these two very different sensibilities have developed independently of each other till modern times.
Even now, art and paintings continue to evolve with speed, with different mediums, styles, and schools of thought. And we will write about more of them in the coming days.
If you have made it through this long essay, great! Congratulations are in order! If you want to know more, recommend you to refer to the Notes & Reference section below for further readings.
Do subscribe to our blog to get updates on new pieces.
About Us:
Paintphotographs.com is India's leading custom art platform. We turn your favorite photos, pics, and images into luxurious handmade portrait paintings. Our work includes handmade portraits, custom oil reproductions, charcoal drawings, and sketches. As a team of accomplished artists, we use museum-quality canvas, best international brands of colors such as Winsor & Newton and Daler Rawney. We work with various mediums, including oil, acrylic, mixed media, graphite, and charcoal.
To order a custom handmade oil portrait painting you can visit our order now page. You can order custom Wedding Paintings, Couple Paintings, Memorial Paintings, Family Paintings, Baby portraits and Children Paintings, Photo to paintings, and Pet Portrait Paintings from Photo.
You can visit our pricing page to know the prices of our portrait paintings. To connect with us ping us on our chat messenger on the website, ping us on WhatsApp, call us at918291070650, or drop us an email at support@paintphotographs.com
You can visit our gallery pages to see our work. We make single portrait paintings, couple paintings, memorial paintings, Kids and Baby Portrait paintings, God & Religious Paintings, Old Photo to Paintings, Wedding couple Paintings & Marriage Portraits, Family Paintings, Pet Portrait Paintings, Radha Krishna Paintings, Oil Portraits of Gurus, Saints & Holy Men, Charcoal and Pencil Sketches, Custom Landscape & Cityscape paintings, Contemporary Art Reproduction & Replica Paintings, Old Master Reproduction & Replica Art, Monochrome and Black & White portrait paintings, Historical Portraits and Shivaji Maharaj Paintings, Celebrity & Political Leaders Portraits. We can also merge separate photos to create a single seamless painting called Composite portraits to add deceased loved ones to make a family oil portrait as though they were present.
Our custom handmade portraits make beautiful Anniversary Gifts, Engagement Gifts, Birthday Gifts, Retirement Gifts, Housewarming Gifts, Mother's Day gifts, and luxurious gifts for many important occasions.
Paintphotographs.com provides bespoke services for art patrons, interior designers, and architects. It helps you create the perfect pieces for residential and commercial projects and serves as a platform for artists to showcase their work.
If you are an art aficionado interested in writing a guest post on art, connect with us.
For sources referenced in the article, please refer to the Notes and Reference section.
Like this story? Then you will love our podcasts on Spotify. Listen to our deep dives and fascinating stories from the art world.
Join our nearly 20,000-strong community on Facebook, WhatsApp, and X.
Want to see our art? Join our community of 500,000+ subscribers on the Paintphotographs YouTube channel, Instagram, and Pinterest for some amazing art pics & art videos!
Notes, References, and Further readings:
https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2006/jun/06/art
https://indianculture.gov.in/ebooks/encyclopaedia-indian-archaeology
https://web.archive.org/web/20050711075630/http://www.iniva.org/archive/resource/1514
https://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/artdok/978/1/Kohle_The_road_from_Rome_to_Paris_2006.pdf
https://books.google.co.in/books?id=2D_ehhO_14QC&pg=PA116&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/poim/hd_poim.htm
https://en-academic.com/dic.nsf/enwiki/111843
https://www.meiselgallery.com/about/the-gallery/
https://artsandculture.google.com/entity/modern-art/m015r61?hl=en
https://www.tate.org.uk/art/art-terms/c/cubism/all-about-cubism
https://www.moma.org/learn/moma_learning/themes/pop-art/
https://www.academia.edu/40244293/R_Siva_Kumar_Modern_Indian_Art_A_brief_overview